What is Plant Tissue Culture?
Plant tissue culture is a technique of growing plant cell, plant tissue, or plant organs in an artificial nutrient medium under aseptic condition. It is one of the fastest methods of growing plantlets in a very short period of time. When many plantlets are grown using a tissue culture technique, then such a method of growing plantlets is called micropropagation. And the plant part that is used in a culture medium for growing plantlets is called explant. Explants can be a root tip, shoot tip, young buds, embryo, anther, or ovary, etc.
Scientists Contribution in Developing Plant Tissue Culture Technique
Haberlandt: He gave the concept of totipotency. And totipotency is the backbone of the tissue culture technique. Totipotency is the ability of each cell in a multicellular organism to develop independently into a new organism. In other words, in a multicellular organism, each cell has got all the information required to develop into a new organism. It is, however, important to mention that Haberlandt only gave the concept of totipotency, but he couldn’t experimentally proof of this concept.
White, Nobe Court, and Glautheret: These three scientists independently did callus culture using tissue culture technique. A callus is an undifferentiated mass of cells.
Skoog and Miller: These two scientists have given great contribution in the tissue culture technique. They used two phytohormones for morphogenesis i.e., for the formation of root and shoot. Callus is an undifferentiated mass of cells. For making plantlets, morphogenesis is required. In other words, there should root and shoot formation in callus. The two phytohormones involved in the process of morphogenesis are auxin and cytokinin.
If in a nutrient medium, auxin concentration is more than cytokinin, then this would promote root formation in callus. On the other hand, if the concentration of cytokinin is more than auxin, then this would promote shoot formation in callus. In other words, if the auxin cytokinin ratio is more, then root formation will take place and if the auxin and cytokinin ratio is less then short formation will take place. What if the auxin and cytokinin concentration are in equal amount, then no differentiation would be found in callus.
Steward: He experimentally proved the concept of totipotency. He developed an embryo without embryoids.
Different Aspects of the Tissue Culture Technique
There are three main aspects of the tissue culture technique. They are mentioned below:
- Nutrient Medium: It is the medium where explant will grow. The nutrient medium could be of two types: liquid medium, or solid medium. For making solid medium, agar or gelatine can be used. The composition of the nutrient medium would include: inorganic salts, vitamins, sucrose (2-4%), amino acid (glycine), auxin (2,4-D), cytokinin (BAP)
- Sterilization: Since the nutrient medium contains sucrose, which is a good medium for the growth of microbes; it is, therefore, important to keep the nutrient medium microbe free. Sterilization is done to make the medium microbe free. There are two types of sterilization techniques: complete sterilization and surface sterilization. Complete sterilization is done for containers, nutrient medium, and instruments. All the components are kept in an autoclave for 15-30 minutes at 130 degrees Celsius. On the other hand, surface sterilization is done for explant. In surface sterilization, common disinfectants are used such as Na-hypochlorite – 1%, chlorine water, hydrogen peroxide – 10%, ethyl alcohol – 70%, and Merthiolate, etc.
- Aeration / Agitation: This is the third aspect of tissue culture technique. Aeration is important for the proper growth of the explant. Agitation of the culture medium is done to ensure there is proper air around the explant.
Types of Tissue Culture
On the basis of nutrient medium, there are two types of tissue culture. They are mentioned below:
- Callus Culture: the explant is cultured in the solid medium where agar is used.
- Suspension Culture: the explant is cultured in a liquid medium
On the basis of explant used – there are four types of tissue culture, which are mentioned below:
- Protoplast Culture: if the explant is used as protoplast (a cell without cell wall), it is called protoplast culture.
- Meristem Culture: If the explant is used as root tip or shoot tip, then it is called meristem culture.
- Anther Culture: if the explant used in tissue culture is anther, then it is called anther culture or pollen culture.
Difference between Callus culture and Suspension Culture: on the basis of nutrient medium
Callus Culture:
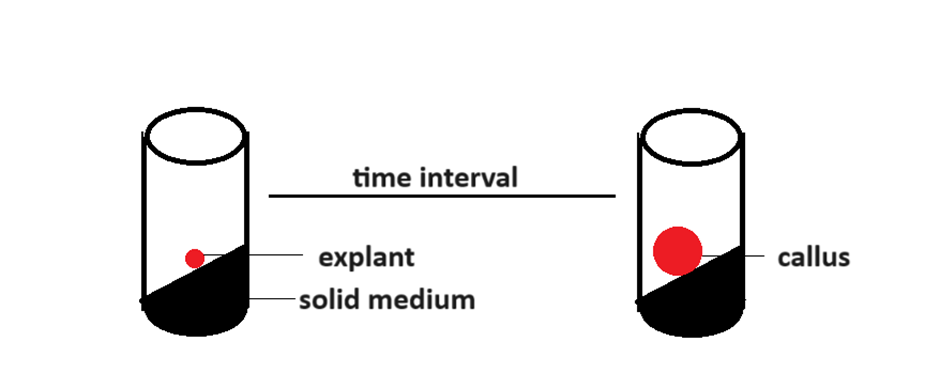
- Explant is grown on a solid medium
- Agar is used for solid medium
- Both auxin and cytokinin are used
- Explant is large in size
- Since, callus is formed in the culture medium, it is called callus culture.
Suspension Culture:
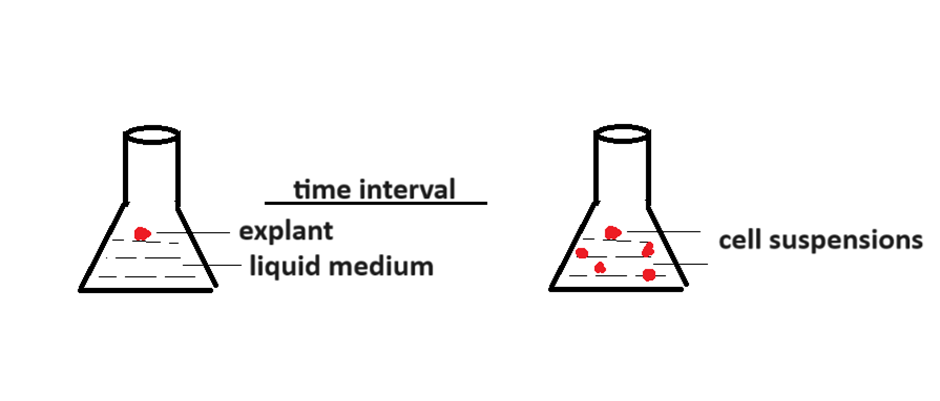
- Explant is grown on a liquid medium
- Agar is absent in the medium
- Only auxin is required
- Explant size is smaller compared to callus culture
- Due to mitotic division in the explant, many suspended cells are formed in the medium and that is why, it is called as the suspension culture.
Formation of Plantlets
There are two methods of formation of plantlets. These two methods are described briefly below:
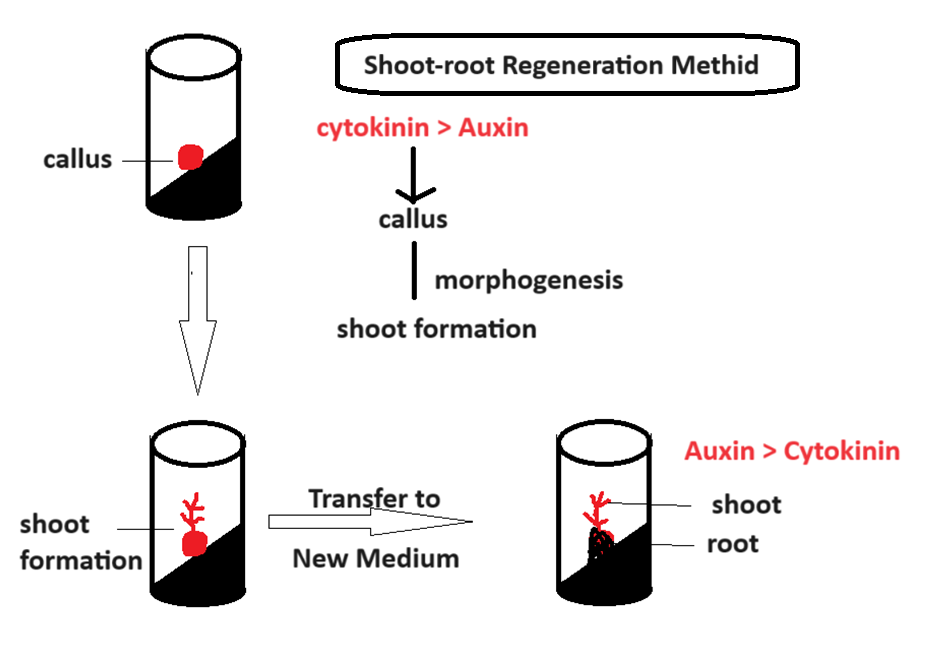
- Shoot-root Regeneration Method: In this method, a solid medium is taken where callus formation has taken place. In this solid medium, the concentration of cytokinin is increased compared to auxin. And since cytokinin is responsible for the formation of shoot, the callus forms shoot. Once the shoot size reaches to 2-3 cm, it is transferred to a fresh medium. In the fresh medium, the auxin concentration is increased compared to cytokinin, and thus root formation takes place. This results in the formation of a plantlet.
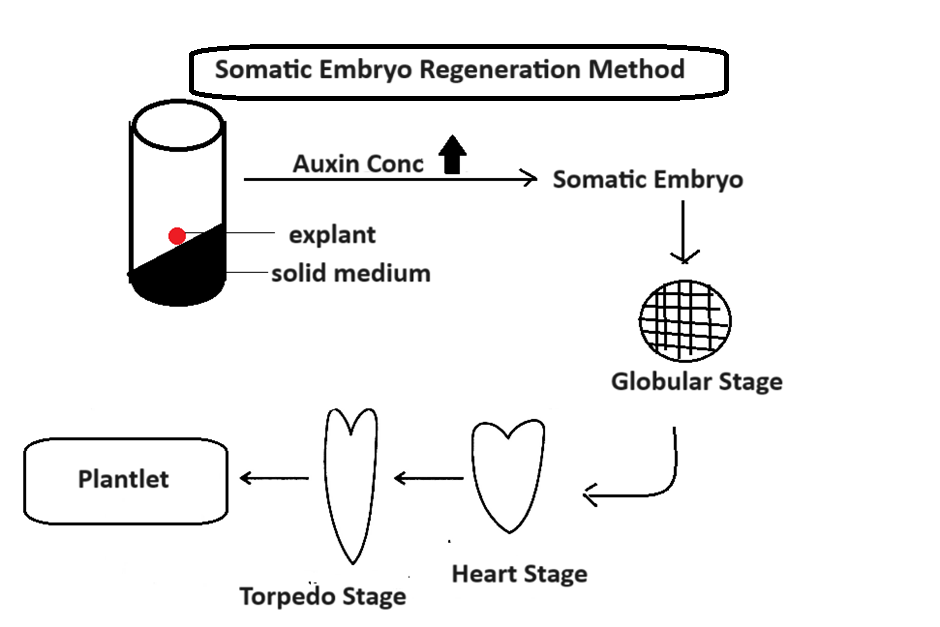
2. Somatic Embryo Regeneration Method:
In this method, the solid suspension containing callus is induced by high concentration of auxin. This results in the formation of somatic embryo. The somatic embryo then develops into globular stage, heart stage and torpedo stage and eventually into a plantlet.
Plant Tissue Culture (On the basis of explant used)
- Protoplast Culture / Somatic Hybridization / Parasexual Hybridization: it is the process of formation of genetically different cells. In order to understand this culture, one need to understand the term protoplast and hybridization. Protoplast is defined as a cell without cell wall. And hybridization is defined as a process of combining two different characters. The purpose of protoplast culture is to combine two superior qualities in one. For instance, if there are two plant varieties: one is having superior fruit quality and the other is having superior pest resistance. Using protoplast culture, both the superior qualities can be combined in one plant.
Technique:
First cells are extracted from two different plant varieties. Generally, mesophyll cells or stem cortex cells are used for this purpose. After cell extraction from two different plant varieties, cells are treated with an enzyme, called cellulase. This results in the digestion of cell wall and the remaining protoplasts are obtained.
After obtaining protoplasts from two different plant varieties, they are fused together. For fusion, two different techniques are used. The first technique is called chemofusion. In this process, chemicals such as PEG (Poly Ethylene Glycol) and PVG are used. The second technique for protoplast fusion is called electrofusion where low-voltage electric pulse is used. After protoplast fusion, the cell obtained is called somatic hybrid cell. The somatic hybrid cell can be of two types depending on what is being fused.
.
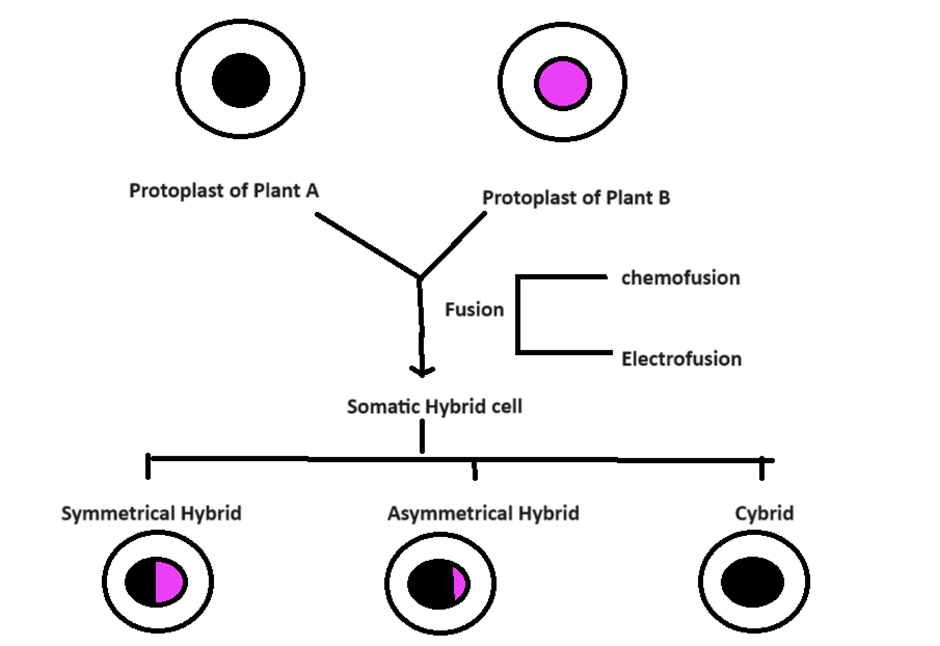
- If both protoplasts are fused completely, then the final hybrid cell obtained will be called as symmetrical hybrid.
- If one complete protoplasm fuses with the other protoplasm’s cytoplasm and a partial nucleus then the hybrid cell obtained will be called as asymmetrical hybrid.
- If one complete protoplasm fuses with the cytoplasm of the other protoplasm only then such hybrid cell obtained will be called as cybrid.
Protoplast culture has been used in plants such as tobacco, tomato, potato, etc. In case of tobacco, two species of tobacco have been used: Nicotiana glauca, and Nicotiana langsdorfii. Pomato has been formed by the fusion of potato and tomato protoplasts.
Embryo Culture Technique
It is a plant tissue culture where the explant is used as embryo. In this technique, embryo is removed from the seed and grown in the nutrient medium to form plantlets. In interspecific hybridization, hybrid seed contain insufficient endosperm to nourish embryo. In such case, embryo is removed and cultured to form plantlets.
Embryo culture technique is used to remove seed dormancy. In case of dormant seeds, embryos are removed from seeds and then cultured in an artificial nutrient medium using the plant tissue culture technique. Embryo culture technique is also used to preserve endangered species of plants.
Meristem Culture Technique
In meristem culture, the explant used is either shoot tip or young buds. The advantage of these explants is that they are virus free. The plantlets formed from meristem culture technique are virus free. However, it is important to note that such plantlets are virus free, but not virus resistant.
Anther Culture Technique / Pollen Culture Technique / Androgenic Culture / Haploid Culture
In this technique, the explant used is immature anther. The plantlets formed through anther culture are haploid in nature. However, it can be made diploid by colchicine treatment. Example: Jinghua No-1 (wheat variety), Guan – 18 (Rice variety).
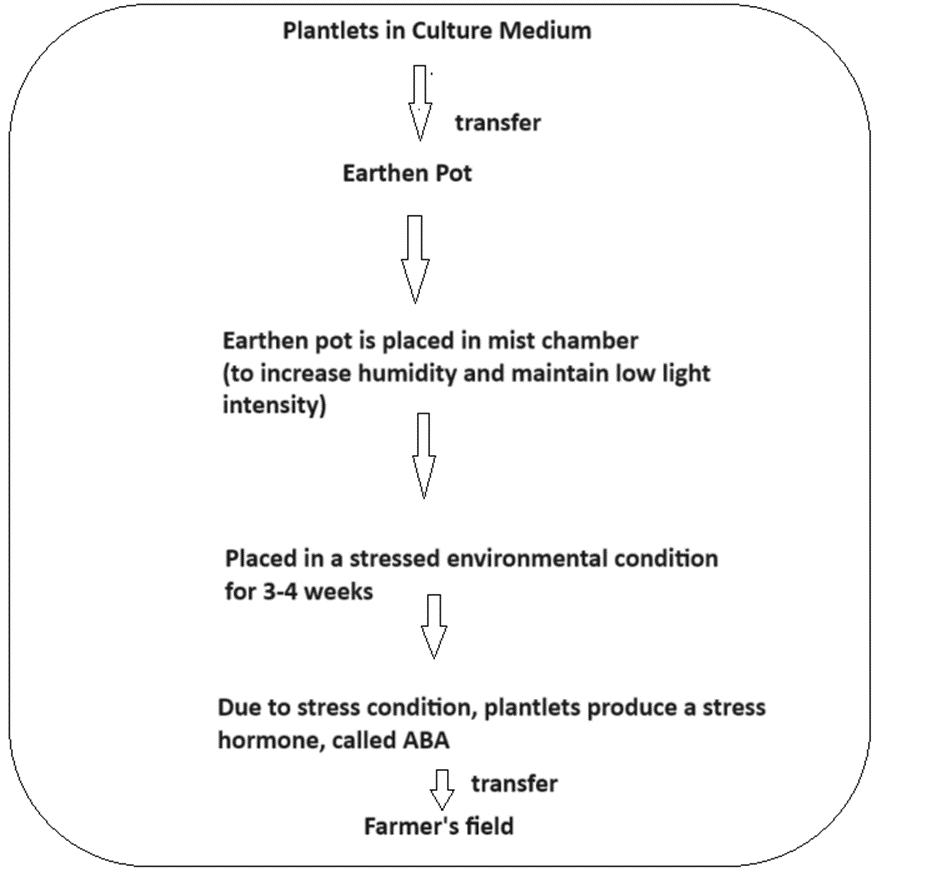
Hardening Procedure
Once plantlets are formed using plant tissue culture technology, they cannot be exposed to the farmers field directly. Plantlets are first exposed to different environmental conditions. The whole process in which plantlets are exposed to different environmental conditions is called hardening. Below is a flow chart that describes the hardening procedure: