In this article of the chapter ecology, we will be discussing the greenhouse effect effortlessly and effectively.
This article will include the concept of greenhouse, greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases, and causes of greenhouse effect – both positive and negative.
Finally, we’ll talk about how to control the negative consequences of the greenhouse effect?
Concept of a Greenhouse
Most of you must have seen a greenhouse. It is a glass house, which is transparent. Inside the greenhouse — plants are grown especially during the winter season.
Now, you must be wondering why is greenhouse used for growing plants, why not in an open agricultural field. Well, in a greenhouse, glass panels let the light in but do not allow heat to escape. You can easily understand this by citing an example of a car that you have parked in an open space for an hour. Once you come back and open the car door, it is heated inside.
In a similar way, since the heat cannot escape from the greenhouse, the temperature inside the house increases. And, plants sensitive to cold temperature can be easily grown inside a greenhouse.
The Mechanism of Greenhouse Effect
Now, when we talk about the greenhouse effect, it has nothing to do with a greenhouse. The term greenhouse is only taken because it causes heating. Similarly, when we talk about the greenhouse effect, we’re talking about the heating of the earth surface and the atmosphere surrounding it. It is important to note that greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that is responsible for heating the earth’s surface and the atmosphere. It is a natural system that has been made by the God.
And if this system had been absent, the earth’s temperature would have been -18°C and it would have been very difficult to survive in such a chilly weather. However, due to greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the earth is 15°C.
Principle behind the Greenhouse Effect
Now, let’s understand the principle behind the greenhouse effect. We all know that the Sun emits solar radiation on the Earth’s surface. We also know that the Sun is a very hot planet. Any object that is hot radiates electromagnetic radiation. And since the Sun is very hot, it will also emit electromagnetic radiation. However, since, it consists of so much energy it will emit short-wave electromagnetic radiation such as UV-rays. It is because, we know the relationship between energy and the wavelength – they are inversely proportional meaning, if the energy is high, wavelength would be shorter and vice versa. Now, let’s consider a simple diagram below to understand the principle of the greenhouse effect.
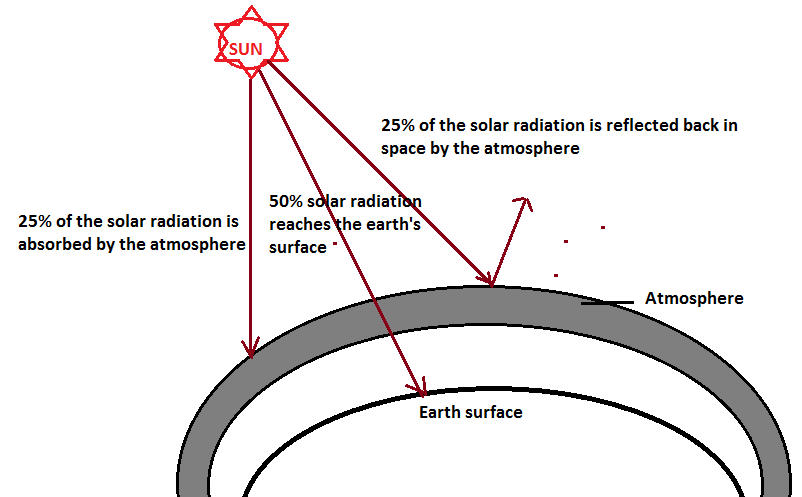
In this diagram, earth is surrounded by atmosphere. And in the Space, Sun is emitting solar radiation or short-wave electromagnetic radiation (UV-rays). Out of the total solar radiation – 25% of the solar radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere, 25% is reflected back by the atmosphere and 50% of the solar radiation reaches the earth’s surface. When the UV-rays hit the earth’s surface – it causes heating of the Earth’s surface. And, as I mentioned earlier, any object upon heating emits electromagnetic radiation so as the Earth. However, the heating is not so much and that’s why, the earth surface re-emits long-wave radiation (Infra-red radiation) rather than a short-wave radiation.
Once infra-red radiation is emitted by the earth’s surface, it strikes the atmosphere where atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide and methane are present. The molecules of these gases radiate heat energy and a major part of it comes to the Earth’s surface thus heating it once again. This cycle is repeated several times. Now, there is a very important term, called the greenhouse gases. These gases allow UV-rays to strike the earth’s surface from Space, but do not allow infra-red radiations to escape from the atmosphere to the Space. Such gases are called greenhouse gases or radiatively active gases. On the other hand, the phenomenon by which the long-wave infra-red radiations hit the earth’s surface from the atmosphere is called greenhouse flux.
Greenhouse Gas Effect and Global Warming
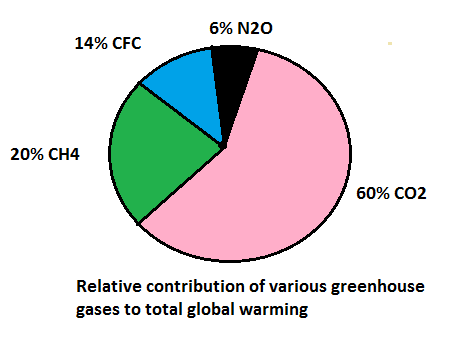
Due to human activities, the level of greenhouse gases is increasing with time leading to considerable heating of the Earth. This has caused GLOBAL WARMING. And in the last three decades, the temperature of the Earth has increased by 0.6 °C. If more greenhouse gases are present in the atmosphere, more infra-red radiations would be absorbed by the gas molecules and more heat energy would be reflected back on the earth surface. Let’s see the relative contribution of various greenhouse gases to total global warming:
Concentration of Greenhouse Gases
| Gases | Concentration |
| CO2 | 368 ppm |
| CH4 | 1750 ppb |
| CFC | 282 ppt |
| N2O | 270 ppb |
A regular assessment of abundance of greenhouse gases and their impact on global environment is being done by IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change).
Effects of Global Warming:
Positive effect:
CO2 Fertilization effect: C3 plants require CO2 concentration of more than 450 ppm while C4 plants require 360 ppm. In other words, C3 plants are dependent on CO2 concentration for the photosynthesis process. Higher the CO2 concentration more will be the photosynthetic rate. Since CO2 concentration is increasing in the environment and therefore C3 plants will have a positive impact on the rate of photosynthesis and this is called CO2 fertilization effect.
Negative effects:
1. In 20th century, the increase in annual mean temperature is 0.6 °C.
2. Due to increase in temperature, odd climatic changes (El Nino effect) have occurred; there is melting of polar ice caps and Himalayan snow caps. In future, this will result in a rise in sea level that can submerge many coastal areas.
3. Due to increase in temperature, organisms living in tropical areas will shift to temperate region; temperate zone organisms will shift to arctic zone and arctic zone organisms will eventually extinct.
How Can We Control Global Warming?
There are certain measures using which we can control global warming. Some of the measures are mentioned below:
- Cut down the use of fossil fuel to save our ecology
- Improve efficiency of energy usage
- Reduce deforestation to save ecology
- Increase planting tress
- Slow down the growth of human population
International conference on global warming was held in Kyoto (Japan) in 1997 where Conference of Parties (CoP-3) initiated Kyoto Protocol under which greenhouse gases would need to be reduced by 5% compared o 1990 and the target was set for 2008 to 2012, which has further been extended till 2020.
In the next article, we’ll discuss the topic: ozone depletion in the stratosphere.
