Fate of Pyruvate
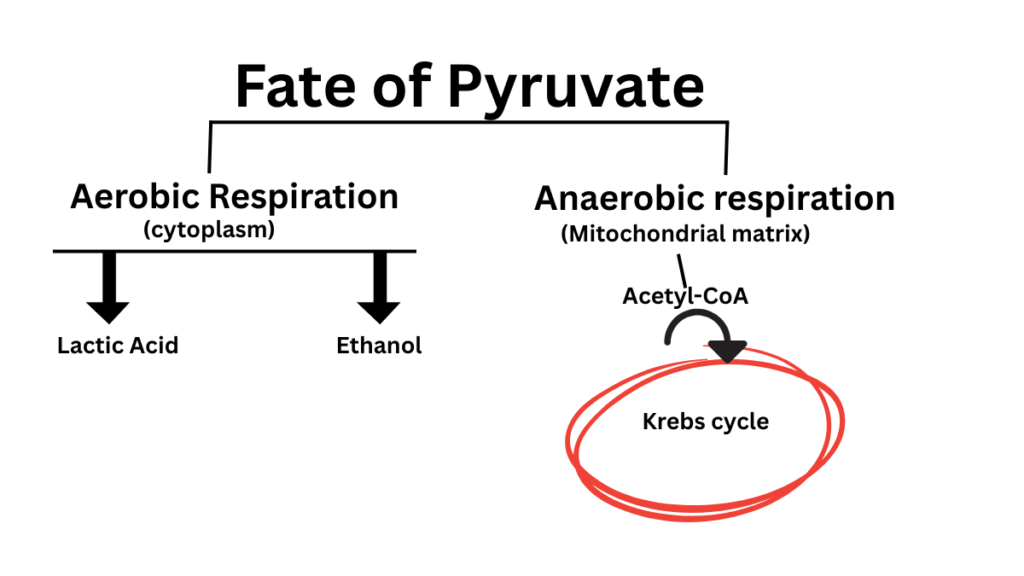
Two molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid) are formed in the 10-step glycolysis pathway. This glycolytic pathway is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. The fate of pyruvate depends on the presence/absence of oxygen, and the type of cells present. For instance, in aerobic conditions and in eukaryotic cells, pyruvate would enter the mitochondrial matrix for further biochemical processing. On the other hand, in anaerobic conditions, pyruvate would form either lactic acid or ethanol in prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic muscle cells. Anaerobic reactions take place in the cytoplasm of a cell. A common term, fermentation, is used for the formation of lactic acid and ethanol.
FERMENTATION
It is an anaerobic respiration process. Glycolysis is common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. The end product of glycolysis is two molecules of pyruvic acid. Let’s see the fate of pyruvic acid in anaerobic respiration.
-
Alcoholic fermentation:
The fate of pyruvate depends on the presence and absence of oxygen. In alcoholic fermentation, the 2 molecules of 3C pyruvic acid undergoes decarboxylation reaction. And the enzyme involved is pyruvate decarboxylase in the presence of TPP and Mg ions. After decarboxylation, 2 molecules of acetaldehyde will be formed. The acetaldehyde will undergo reduction (addition of H and e) by NADH2 in the presence of alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme. After reduction, 2 molecules of ethyl alcohol and 2 NAD+ will be formed. It is important to remember that 2 molecules of NADH2 formed in glycolysis have been used up in the fermentation process. Example: yeast. If the alcohol concentration in the yeast cell reaches to 13%, this would cause the yeast cell to die. Wine and beer can be formed through alcoholic fermentation, but if the drinks having higher alcohol concentration, this fermentation cannot be used rather an artificial method would be needed like distillation. Example, whisky, rum, vodka, etc.
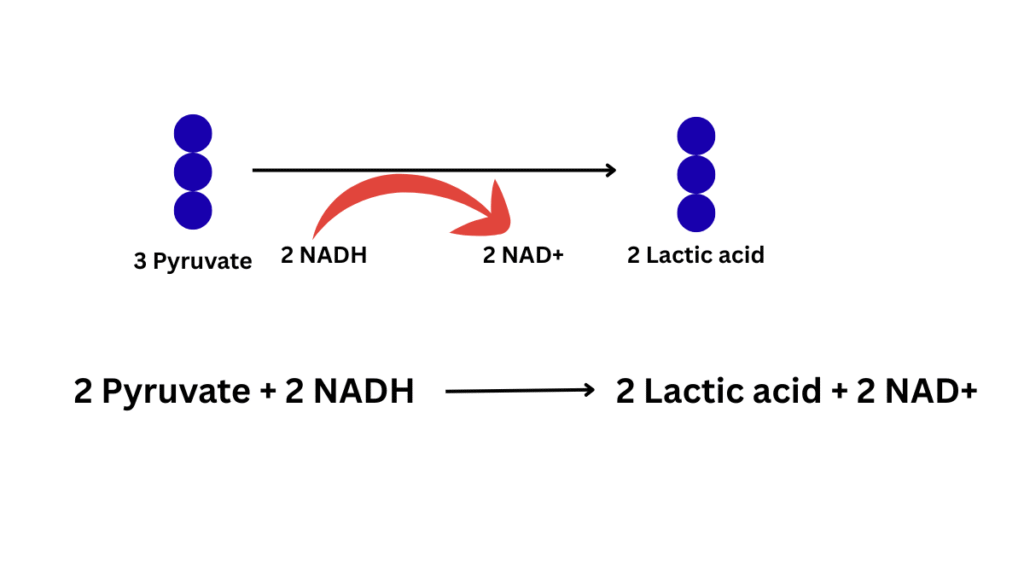
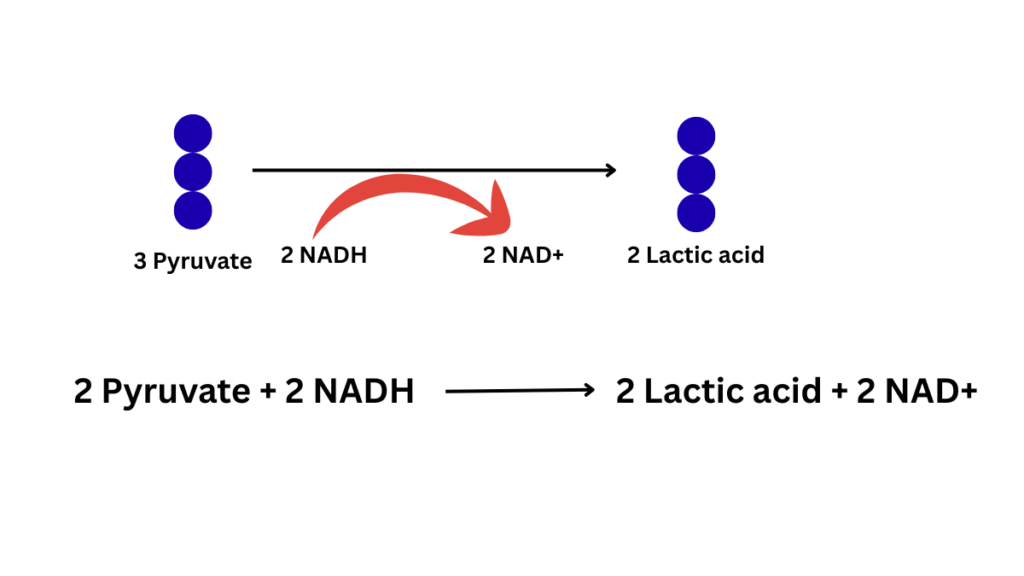
2. Lactic acid fermentation:
The fate of pyruvate depends on the presence and absence of oxygen. Direct reduction of pyruvic acid will occur leading to the formation of two molecules of CH3-CHOH-COOH (lactic acid) in the presence of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (present in the cytoplasm) in the presence of FMN and Zn. Here, for reduction NADH2 will be utilized. Example: bacteria (LAB), muscles. Lactic acid fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell. It can occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (muscle cells).
Note: in fermentation, the net ATP production is 2ATP. The net water released is zero. It is important to note that the total energy produced during aerobic respiration is 686 Kcal. In alcoholic fermentation, it is 58 Kcal and in lactic acid fermentation, it is 36 Kcal.
The efficiency of alcoholic fermentation = 58 / 686 x 100 = 8.4%
The efficiency of lactic acid fermentation = 36 / 686 x 100 = 5.2%
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions): Fate of Pyruvate
Q. What conditions are required for the fermentation of glucose in yeast?
A. In yeast, fermentation involves the incomplete oxidation of glucose achieved under anaerobic conditions (the absence of oxygen).
Q. Which enzymes facilitate the conversion of pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide?
A. The reactions that convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide () and ethanol are catalysed by the enzymes pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
Q. How does the fermentation process in some bacteria differ from that in yeast?
A. While yeast produces ethanol and , some organisms, such as certain bacteria, produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid.
Q, Under what circumstances do animal cells perform fermentation?
A.Animal cells, specifically muscles during exercise, produce lactic acid when oxygen is inadequate for cellular respiration.
Q. What is the role of NADH+ in lactic acid and alcohol fermentation?
A. NADH+ acts as a reducing agent during the reduction of pyruvic acid. In both processes, it is reoxidised to NAD+.
Q. How efficient is fermentation in terms of energy release?
A. Fermentation is not very efficient; less than seven per cent of the energy stored in glucose is released, and not all of it is trapped as high-energy bonds of ATP.
Q. Why are fermentation processes considered hazardous to the organisms?
A.The processes are hazardous because they result in the production of substances that can be harmful to the cell, specifically acid or alcohol.
Q. What is the maximum alcohol concentration yeast can survive during natural fermentation?
A.Yeast cells poison themselves to death when the alcohol concentration reaches approximately 13 per cent.
Q. What characterizes aerobic respiration compared to fermentation?
A. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic substances in the presence of oxygen. Unlike fermentation, it releases , water, and a large amount of energy present in the substrate.
Q. Where does the complete oxidation of glucose occur in eukaryotic cells?
A. In eukaryotes, the steps for complete oxidation of glucose take place within the mitochondria and require oxygen (O2)