What is Southern Blotting?
What is Southern Blotting? Why and how it is done? First of all, we need to understand the word “Southern” – well, this word has come after the name of the scientist Edward M Southern who first developed this Southern Blotting technique at Edinburgh University, United Kingdom in the 1970s. Now, what is the meaning of blotting? In this word, blot means membrane. In order to perform Southern Blotting, we need to use a special type of membrane on which molecules such as DNA, RNA or proteins could get attached to it. The process of transferring DNA, RNA or proteins from get to the membrane is called blotting. If we want to analyze DNA – we need to use Southern Blotting technique. Likewise, for RNA and proteins – we need to perform Northern blotting and Western blotting techniques respectively.
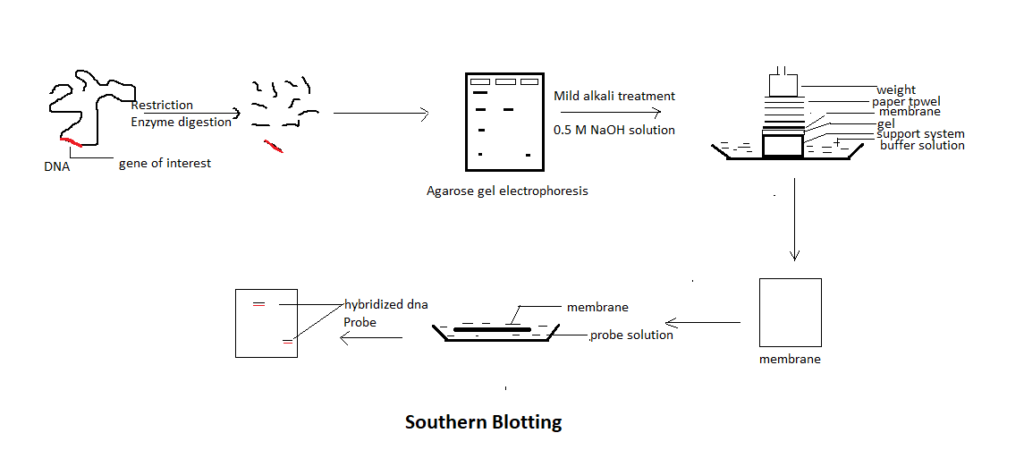
Procedure of Southern Blotting
Now, the question is why and how Southern Blotting technique is performed? Southern blotting technique is performed to find a specific sequence of DNA within a complex mixture. In other words, we can say that it is a technique of finding gene of interest within an entire genome. The sequence of the gene is already known to us and what restriction sites are present near the gene sequence is also known beforehand. Since, we know the restriction sites on the DNA present near the gene of interest – we use specific restriction enzyme to digest the genome. Once restriction enzyme is added to the genome, it cuts DNA into small fragments. Out of the many DNA fragments – one fragment could be our gene of interest. Now, the question is how to analyze this gene of interest, which is mixed in so multiple DNA fragments? It is like finding a needle in a haystack.
Separation of Multiple DNA Fragments using Gel Electrophoresis
In order to separate multiple DNA fragments, gel electrophoresis is performed. In this procedure, DNA fragments are run in an agarose gel medium to separate DNA fragments on the basis of their respective molecular weight. However, the separated DNA fragments remain as double stranded DNA. The double stranded DNA needs to be converted into single stranded DNA.
Denaturation of Double Stranded DNA
To denature double stranded DNA fragments into single stranded DNA fragments – mild alkali treatment is given. The gel is soaked in about 0.5M NaOH solution. Once the gel is soaked in the alkali solution – the hydrogen bonds present between two DNA strands break and double stranded DNA gets converted into single stranded DNA.
Transfer of Single Stranded DNA from Gel to the Nitrocellulose Membrane
For transferring gel on the nitrocellulose paper, we need a tray and it is filled with a transfer buffer solution. After that a support system is prepared before the DNA containing gel is transferred to the nitrocellulose paper. For the support system, we generally use either glass or sponges. On the support system, gel containing DNA is transferred. On top of the gel, nitrocellulose or nylon membrane of the same size of the gel is used. In a majority of cases, nylon membrane is used because nylon is a strong membrane and it binds with DNA molecules quite tightly. On top of the membrane, paper towels are kept and some weight is used at the top so that paper towel could press the membrane and the gel containing DNA fragments. Once the setup is done – the transfer buffer present in the tray move upward due to capillary action. Once it reaches the gel surface – DNA fragments present in the gel also move upward towards the membrane. And finally, the DNA fragments present in the gel get attached to the membrane. Once paper towels get wet completely – it means, the transfer process has completed. After that the membrane is removed. Though DNA fragments have been transferred on the nylon / nitrocellulose membrane, but nothing is visible on the membrane. First, the membrane is either given heat treatment or UV light treatment to fix the membrane and the DNA.
The nylon / nitrocellulose membrane is incubated in a probe solution. For this purpose, a tray is taken with probe solution in which membrane is placed. This solution contains probes – short oligonucleotide sequence. The probe is attached to a detector at one end. The detector could either be a radiolabelled atom or fluorescent molecules. The oligonucleotide sequence in the probe is the complementary sequence of the gene of interest (since we know the gene sequence of the gene of interest). If the membrane containing DNA fragments contain gene of interest fragment then the probe will hybridize with that gene segment.
Once hybridization is done – nothing is visible on the membrane. However, based on the detector molecule used in the probe, we use different methods to visualize the hybridized DNA present on the membrane. For instance, if the detector is radiolabelled, then we use autoradiography for visualization. If the probe fluorescently tagged then after binding, it shows fluorescence which can be measured to detect whether the gene of interest has hybridized with the probe or not.
Application of Southern Blotting
Southern blotting is used in a number of applications in the field of molecular biology. One of the primary applications of Southern blotting is to identify a specific gene in a DNA sample. This is done to identify viral and bacterial infections. In recombinant DNA technology, it is used to identify and isolate a particular gene of interest. It is also used in DNA fingerprinting for paternity testing, victim and criminal identification.
