Q1. Which of the following process keeps species continue to live through millions of years?
- Evolution
- Reproduction
- Mutation
- All of the above
Ans: b
Q2. Which of the following defines life span?
- It is the period from birth to natural death of an organism
- It is the total time a person has lived on earth
- It is the average age of survival in human beings
- None of the above
Ans: a
Q3. Life spans of organisms are not necessarily correlated with their sizes: the size of crow and parrots are almost same yet their life spans are:
- 15, 140 years
- 25, 100 years
- 15, 110 years
- 30, 150 years
Ans: a
Q4. Mango and Peepal are almost similar in size, but their life spans differ significantly. The life spans of mango and peepal are:
- 200, 2500 years
- 100, 1000 years
- 150, 15000 years
- 200, 3000 years
Ans: a
Q5. The life spans of cow and dog are respectively:
- 25, 50 years
- 25, 25 years
- 30, 25 years
- 50, 25 years
Ans: b
Q6. Which of the following organism has a life span of one month?
- Butterfly
- May fly
- Fruit fly
- Cicada
Ans: c
Q7. Which of the following organism has the maximum life span?
- Rice
- Banana tree
- Banyan tree
- Peepal tree
Ans: d
Q8. Which of the following organism has the shortest life span?
- May fly
- Butter fly
- Fruit fly
- Rice plant
Ans: a
Q9. Which of the following organism is considered as immortal?
- Single-celled eukaryotes
- Multicellular eukaryotes
- Single-celled prokaryotes
- Multicellular prokaryotes
- Both a and c
Ans: e
Q10. The life cycle of an organism consists of stages such as:
- Birth
- Growth
- Death
- All of the above
Ans: d
Q11. The kind of reproduction an organism would perform depends on:
- The organism’s habitat
- The organism’s internal physiology
- Both a and b
- None
Ans: c
Q12. An asexual reproduction is defined as a type of reproduction in which:
- Only single parent is involved i.e., uniparental
- Gamete may or may not be formed
- No fusion of gametes
- All of the above
Ans: d
Q13. A sexual reproduction is defined as a type of reproduction in which
- Two parents are involved
- Gamete formation is essential
- Fusion of gametes is essential
- All of the above
And: d
Q14. The offspring produced through asexual reproduction are:
- Morphologically and genetically identical
- They can be called as clone
- Both a and b
- Morphologically and genetically different
Ans: c
Q15. In which of the following phylum, cell division (binary fission) is itself a mode of reproduction?
- Monera
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Both a and b
Ans: e
Q16. Conidia (asexual spores) are formed in which of the following organisms?
- Hydra
- Sponges
- Penicillium
- Unicellular alga
Ans: c
Q17. Choose the correct sequence of structures from bottom to top in the formation of conidia?
- Conidiophore — > Rami — > Metulae — > Sterigmata — > conidia
- Conidiophore — > Metulae — > Rami — > Sterigmata — > conidia
- Metulae — > Rami — > Conidiophore — > sterigmata — > conidia
- Rami — > Metulae — > Sterigmata — > conidiophores — > conidia
Ans: a
Q18. Mitospores are present in which of the following groups of organisms?
- Fungi
- Algae
- Both a and b
- Bryophytes
Ans: c
Q19. Gemmules are formed by:
- Sponges
- Hydra
- Penicillium
- Chlamydomonas
Ans: a
Q20. Under unfavorable condition, amoeba withdraws its pseudopodia and secretes a three-layered hard covering. This phenomenon is called:
- Excystation
- Encystation
- Sporulation
- None of the above
Ans: b
Q21. On the onset of favorable condition, the encysted amoeba divides by multiple fission to produce many minute amoebae or pseudopodiospores. The cyst wall bursts out and the spores are liberated in the surrounding medium to grow up into many amoebae. This phenomenon is called:
- Excystation
- Encystation
- Sporulation
- None
Ans: c
Q22. Read the following options and choose the correct statement from the following:
- Binary fission involves equal division while budding involves unequal division
- Binary fission does not show the formation of protuberance while budding shows protuberance
- In binary fission, the parents cell disappear while in budding, the parent cell exists even after division
- Binary fission and budding are present in amoeba and hydra respectively
- I, ii correct
- I, ii, iii correct
- I, ii, iii, iv correct
- I, iii, iv correct
Ans: c
Q23. Which type of binary fission is present in paramecium?
- Simple binary fission
- Longitudinal binary fission
- Transverse binary fission
- Multiple binary fission
Ans: c
Q24. In plants, units of vegetative propagation include:
- Sucker
- Runner
- Offset
- Bulb
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q25. Which of the following underground stem modification for vegetative propagation shows branching?
- Rhizome
- Corm
- Tuber
- Bulb
Ans: a
Q26. Which of the following underground stem modification does not have adventitious roots?
- Rhizome
- Corm
- Tuber
- Bulb
Ans: c
Q27. The terror of Bengal that grows in standing water is:
- Eicchornia
- Water hyacinth
- Both a and b
- None
Ans: c
Q28. Eicchonia is propagated through sub aerial stem modification, called:
- Stolon
- Sucker
- Offset
- Runner
Ans: c
Q29. Which of the following plants are propagated through bulbil?
- Dahlia
- Agave
- Potato
- Ginger
Ans: b
Q30. Morphologically and genetically identical offspring cannot be obtained from:
- Stem cutting
- Sporulation
- Budding
- Zygote
Ans: d
Q31. Which of the following mode of reproduction is present in organisms having relatively simple organization?
- Asexual mode of reproduction
- Sexual mode of reproduction
- Both a and b
- None
Ans: a
Q32. Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
- Yeast – zoospores
- Chlamydomonas – conidia
- Onion – bulb
- Ginger – sucker
Ans: c
Q33. Consider the figure given below and choose the correct statement regarding asexual reproduction:
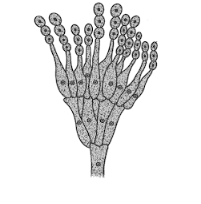
- Microscopic non motile spores
- Always formed under unfavorable condition
- Condia are arranged in acropetal succession
- Exogenously produced meiospores
Ans: a
Q34. How sexual reproduction in organisms like algae and fungi enables these organisms to survive during unfavorable conditions?
- Sexual reproduction is biparental so the offspring would be morphologically and genetically be variant
- Sexual reproduction is biparental so the offspring would be morphologically and genetically be similar
- Sexual reproduction is a complex process
- None
Ans: a
Q35. Which of the following statement is true for sexual reproduction?
- Sexual reproduction involves formation of the male and female gametes, either by the same individual of by different individuals of the opposite sex
- Because of fusion of male and female gametes, sexual reproduction results in offspring that are not identical to the parents
- Sexual reproduction is a complex process
- Through sexual reproduction, less number of progeny is formed
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q36. Sexual reproduction involves in the formation and fusion of gametes. This process involves mostly two parents, but can be uniparental as seen in:
- Leeches
- Tapeworm
- Both a and b
- Roundworm
Ans: c
Q37. Organisms like plants, animals and fungi though differ so greatly in external features, internal structures and physiology, when it comes to sexual mode of reproduction, they share a similar pattern. Which of the following phases are common in these organisms?
- Juvenile / vegetative phase
- Reproductive phase
- Senescence
- All of the above
Ans: d
Q38. Monocarpic plants:
- Are always annuals or biennials
- After reaching maturity flower repeatedly at regular intervals
- May be perennial
- Are exemplified by mango and bambusa
Ans: c
Q39. Inter-flowering period of a polycarpic plant represents:
- Vegetative phase
- Senescence phase
- Recovery phase
- Juvenile phase
Ans: c
Q40. The end of juvenile phase marks the beginning of:
- Recovery phase
- Senescence phase
- Vegetative phase
- Period of maturation phase
Ans: d
Q41. Which of the following plant flowers once generally after 50-100 years?
- Mango
- Bamboo
- Cactus
- Strobilanthus kunthiana
Ans: b
Q42. There are three phases in the lifecycle of an organism. The longest vegetative phase is seen in:
- Strobilanthus
- Bambusa
- Hibiscus
- Mango
Ans: b
Q43. Which of the following plant flowers in every 12 years during September-October in the hilly areas of Kerela, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu?
- Bamboo
- Cactus
- Cassia
- Strobilanthus kunthiana
Ans: d
Q44. Statement A- the longest vegetative phase is seen in bambusa
Statement B – Bambusa is a perennial monocarpic plant
- Only A is correct
- Only B is correct
- Both A and B are correct
- Both A and B are incorrect
Ans: c
Q45. Sexual reproduction is an elaborate, complex, and slow process. Which of the following statement is not true with respect to sexual reproduction?
- It can be uniparental
- Involves meiosis and syngamy
- Offspring are identical to the parents
- All organisms have to reach a certain stage of growth and maturity in order to reproduce sexually
Ans: c
Q46. All sexually reproducing organisms exhibit events and processes that have remarkable fundamental similarity even though the structures associated with sexual reproduction are indeed very different. The events of sexual reproduction though elaborate and complex, follow a regular sequence. These sequential events are:
- Pre-fertilization — > fertilization — > post-fertilization
- Fusion — > zygote formation — > embryogenesis
- Pre-fertilization — > post-fertilization
- All of the above
Ans: a
Q47. Which of the following is not a pre-fertilization event in flowering plant?
- Gamete formation
- Development of male gametophyte
- Pollen germination
- Vivipary
Ans: d
Q48. The two main prefertilization events include:
- Gametogenesis and pollination
- Gametogenesis and gamete transfer
- Tissue differentiation and syngamy
- Gamete transfer and syngamy
Ans: b
Q49. Pollination is considered under which of the following events in sexual reproduction?
- Pre-fertilization
- Fertilization
- Post-fertilization
- None of the above
Ans: a
Q50. Parthenogenesis is considered under which of the following events in sexual reproduction?
- Pre-fertilization
- Fertilization
- Post-fertilization
- None of the above
Ans: b
Q51. Zygote is considered under which of the following events in sexual reproduction?
- Pre-fertilization
- Fertilization
- Post-fertilization
- None of the above
Ans: c
Q52. Which of the following are the main pre-fertilization events?
- Gametogenesis
- Gametic transfer
- Gametic fusion
- Both a and b
Ans: d
Q53. Isogametes (Homogametes) are found in:
- Cladophora
- Fucus
- Homo sapiens
- All of the above
Ans: a
Q54. Which of the following organisms produce heterogametes?
- Fucus
- Marchantia
- Pteris
- Cycas
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q55. Which of the following options do not show homogametic condition?
- Cladophora
- Chlamydomonas
- Synchytrium
- Fucus
Ans: d
Q56. A unisexual flower is said to be monoecious when:
- Both male and female sex organs are present in the same flower of a plant
- Both male and female sex organs are present in separate flowers of the same plant
- Both male and female sex organs are present in separate flowers in different plants
- None of the above
Ans: b
Q57. Which of the following is an example of monoecious plant?
- Cucurbits
- Coconut
- Both a and b
- Papaya
Ans: c
Q58. Find the odd choice out of the following with respect to sexuality:
- Monoecious
- Homothallic
- Dioecious
- Bisexual
Ans: c
Q59. Which of the following pair of plants show monoecious condition?
- Papaya and date palm
- Castor and cucurbits
- Papaya and castor
- Date palm and coconuts
Ans: b
Q60. Which of the following organisms are considered as hermaphrodite?
- Earthworm
- Sponges
- Tapeworm
- Leech
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q61. Which of the following pairs are correct with respect to their meanings?
- Dioecious, bisexual
- Dioecious, hermaphrodite
- Monoecious, hermaphrodite
- Monoecious, unisexual
Ans: d
Q62. Which of the following statement is true in relation to sexuality in Chara?
- Chara possess monoecious condition where female sex organ is present above the male sex organ
- The female sex organ in Chara is flask shaped, jacketed and referred as oogonium or nacule
- The male sex organ in Chara is round shaped, jacketed and referred as antheridium or globule
- The female sex organ produces a single egg while male sex organ produces many spirally coiled and biflagellated male gamete
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q63. Identify A and B in the following diagram:
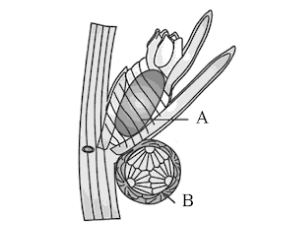
- Chara – red algae A= Globule; B = Nucule
- Chara – green algae A = Globule; B = Nucule
- Chara – Nonvascular embryophyte A = Nucule; B = Globule
- Chara – stone wart A = nucule as female sex organ; B = Globule as male sex organ
Ans: d
Q64. Read the following statements with respect to the diagram and select the correct set of option:
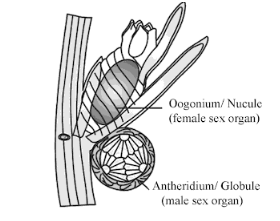
- Member of class chlorophyceae
- Dioecious plant body
- Sex organs are multicellular and jacketed
- Homogametes
- Gametophytic plant body
- External fertilization
- A, C and E are correct
- All correct except D
- A, B, C and E are correct
- A, B, C and F are correct
Ans: a
Q65. Which of the following represents a dioecious plant?
- Papaya
- Date palm
- Both a and b
- Coconut
Ans: c
Q66. Which of the following possess meiocytes?
- Haploid cells
- Diploid cells
- Gamete mother cells
- Both b and c
Ans: d
Q67. Chromosome number in gametes of sugarcane and rice is respectively:
- 12, 40
- 40, 12
- 80, 24
- 24, 12
Ans: b
Q68. In rice, a meiocyte has 24 chromosomes. What will be the number of chromosomes in its somatic cell?
- 24
- 12
- 48
- 6
Ans: a
Q69. In which of the following groups of organisms, both the types of gametes are motile?
- Algae and bryophytes
- A few fungi and algae
- Bryophytes and pteridophytes
- Algae and vascular embryophytes
Ans: b
Q70. In which of the following organisms, male gamete is flagellated in nature?
- Algae and some fungi
- All bryophytes
- All pteriodophytes
- All of the above
Ans: d
Q71. Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen from male flower to the stigma of female flower. This process occurs in:
- Bisexual plants
- Monoecious plants
- Dioecious plants
- Both b and c
Ans: d
Q72. Parthenogenesis is a phenomenon in which the female gamete undergoes development to form new organisms without fertilization. Which of the following organisms show this phenomenon?
- Rotifers
- Honeybees
- Lizards
- Birds (turkey)
- All of the above
Ans: e
Q73. Which of the following organisms show external fertilization?
- Algae
- Fishes
- Amphibians
- All of the above
Ans: d
Q74. Out of the following species, how many shows internal and how many show external fertilization?
Spirogyra, Chara, Ulothrix, Polysiphonia, Marchantia, Pinus
- 5, 1
- 4, 2
- 3, 3
- 1, 5
Ans: a
Q75. Which of the following is considered as the vital link that ensures the continuity of species between organisms of one generation and the next?
- Gamete
- Embryo
- Zygote
- Spores
Ans: c
Q76. Which among the following is not a post-fertilization event?
- Morphogenesis
- Gametogenesis
- Embrygenesis
- Fruit formation
Ans: b
Q77. During embryogenesis, embryo undergoes:
- Mitotic cell division and cell differentiation
- Meiotic cell division and cell differentiation
- Mitotic cell division only
- Meiotic cell division only
Ans: a
Q78. Which of the following option does not fit with respect to post-fertilization events in the life cycle of a flowering plant?
- Embryogenesis
- Morphogenesis
- Pollination
- Fruit and seed formation
Ans: c
Q79. During embryogeny, zygote undergoes:
- Meiotic division immediately
- Cell division only
- Cell differentiation only
- Both cell division and cell differentiation
Ans: d
Q80. Basal half of an onion bulb is removed and upper half is sown in the ground. New plant will:
- Emerge normally
- Not emerge
- Be without leaves
- Be without flowers
Ans: b
Q81. What is essential for a successful grafting to occur?
- Each section must be able to form root
- The grafted section must be able to form seeds
- Fusion of two vascular tissue must occur
- Fusion of two cambial tissue must occur
Ans: d

Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is fantastic blog. A great read. I’ll certainly be back.